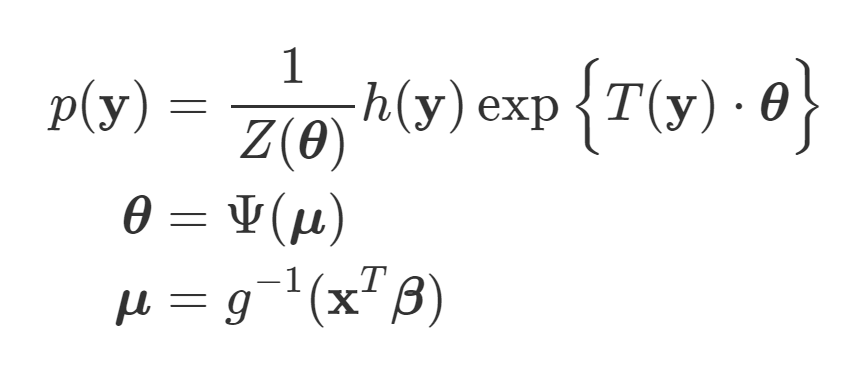-
Writing
-
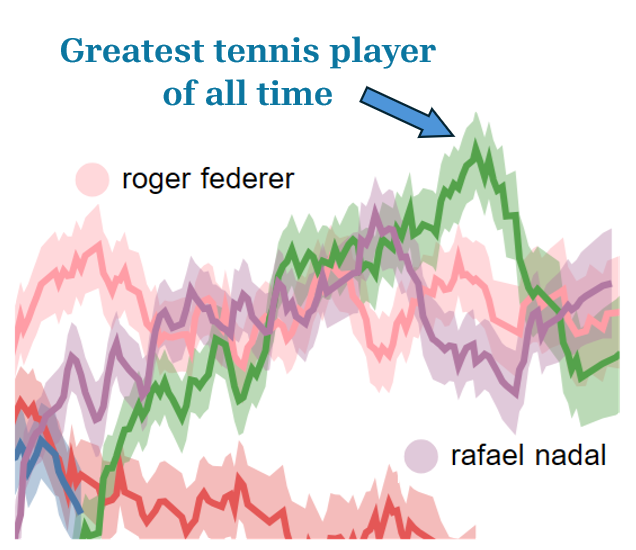
- TrueSkill Part 2: Who is the GOAT?
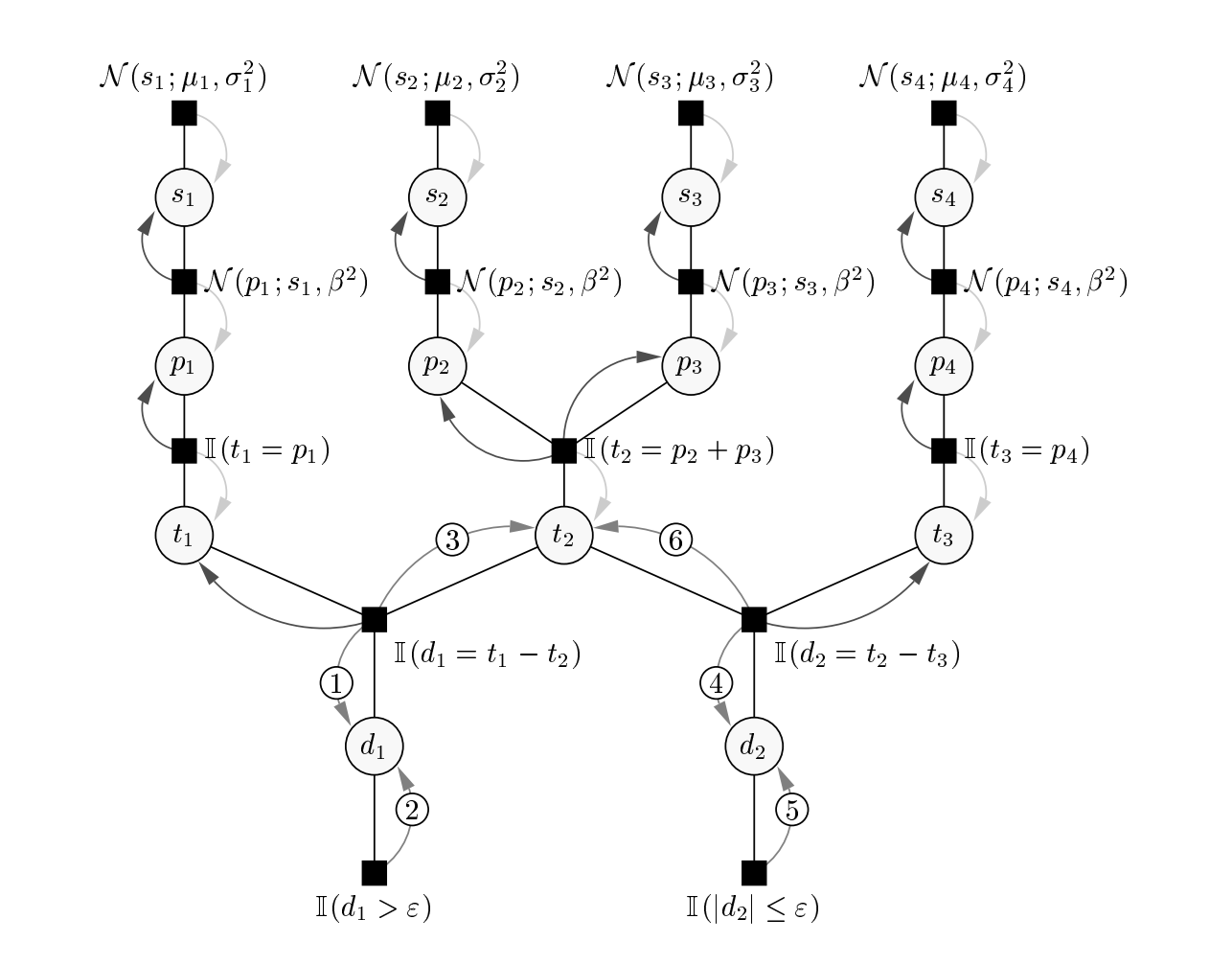
- TrueSkill Part 1: The Algorithm
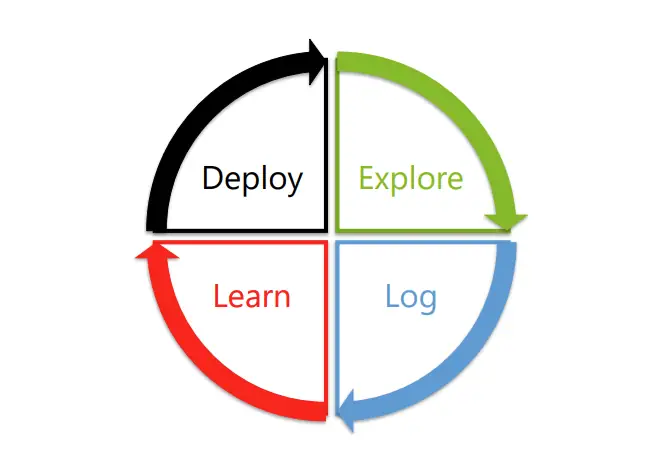
- Algorithmic Operations: Lessons from Bandit Algorithms
- When does the Delta Method approximation work?
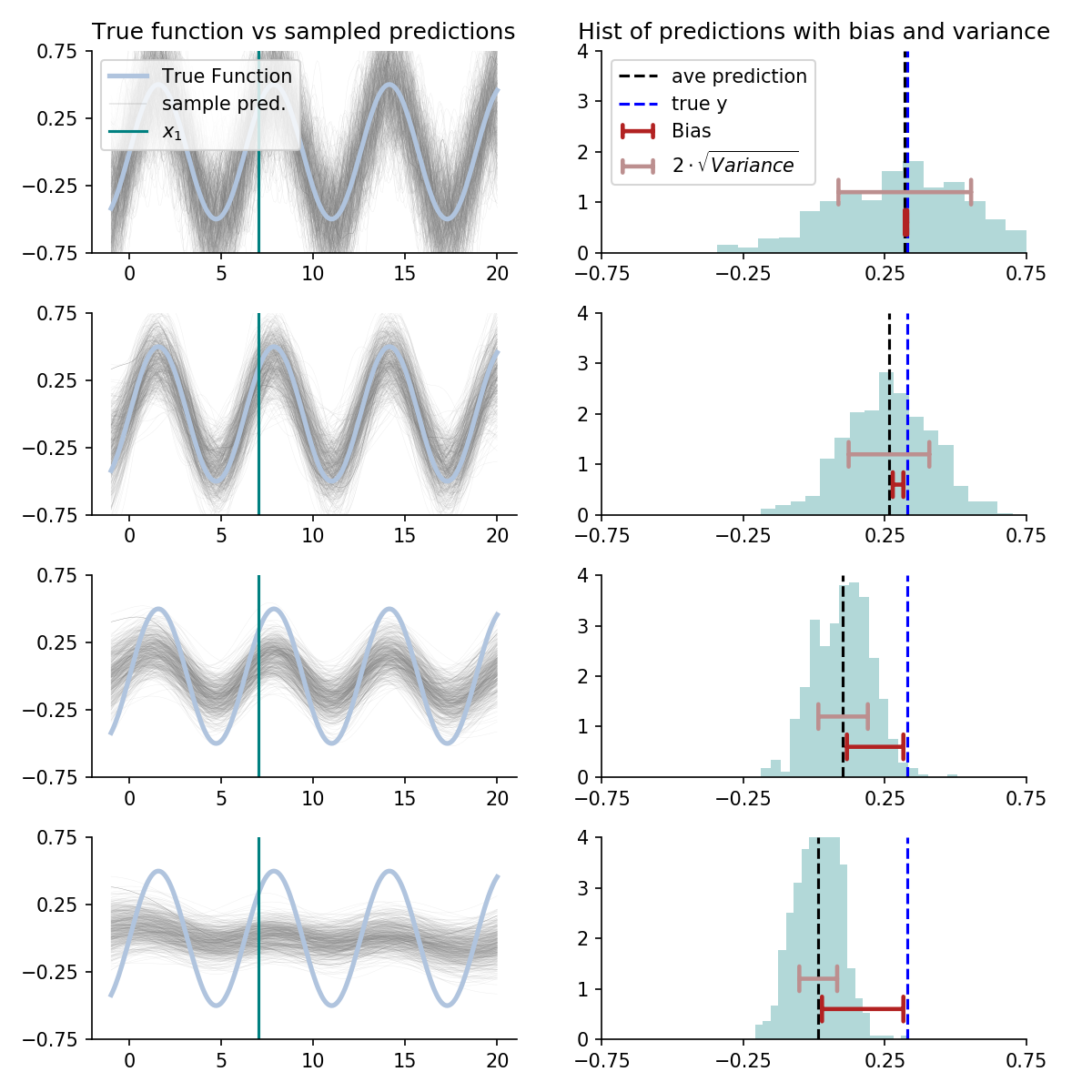
- Bias-Variance Trade-Off
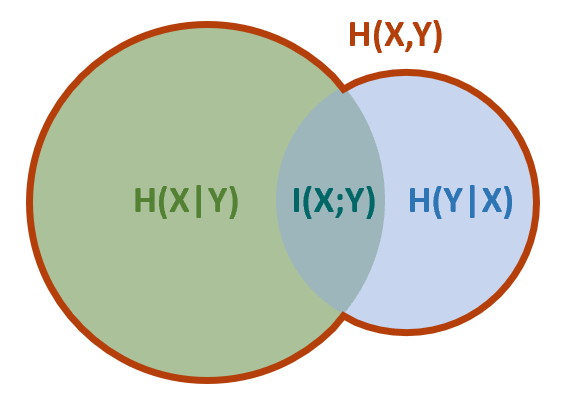
- Information Theory and Entropy
- Generalized Linear Models
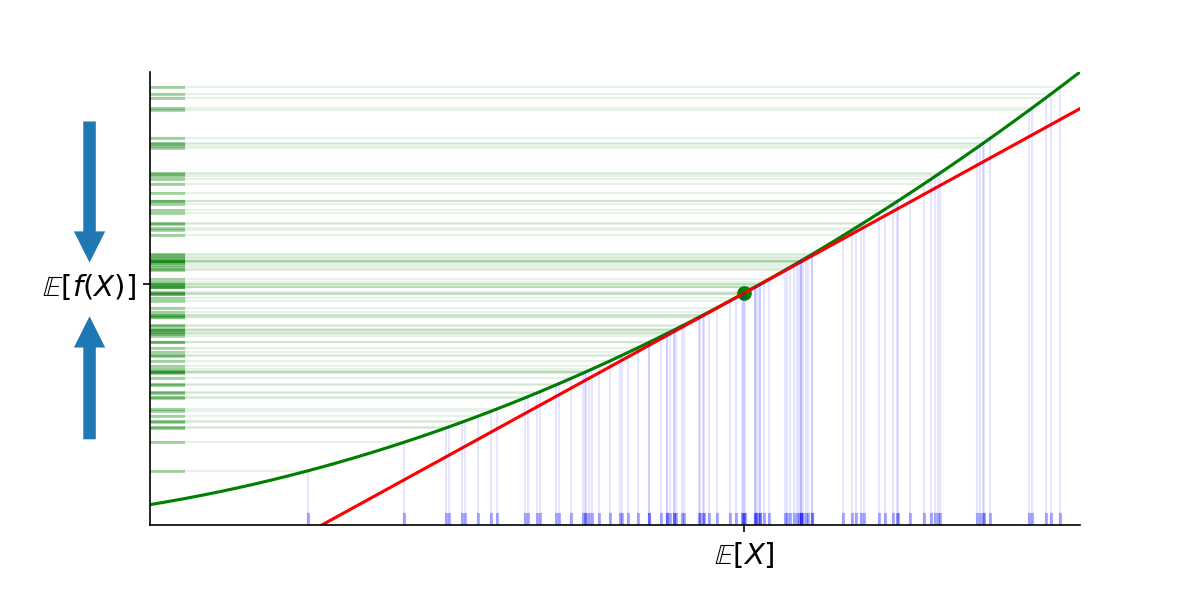
- Jensen's Inequality
- The Fisher Information
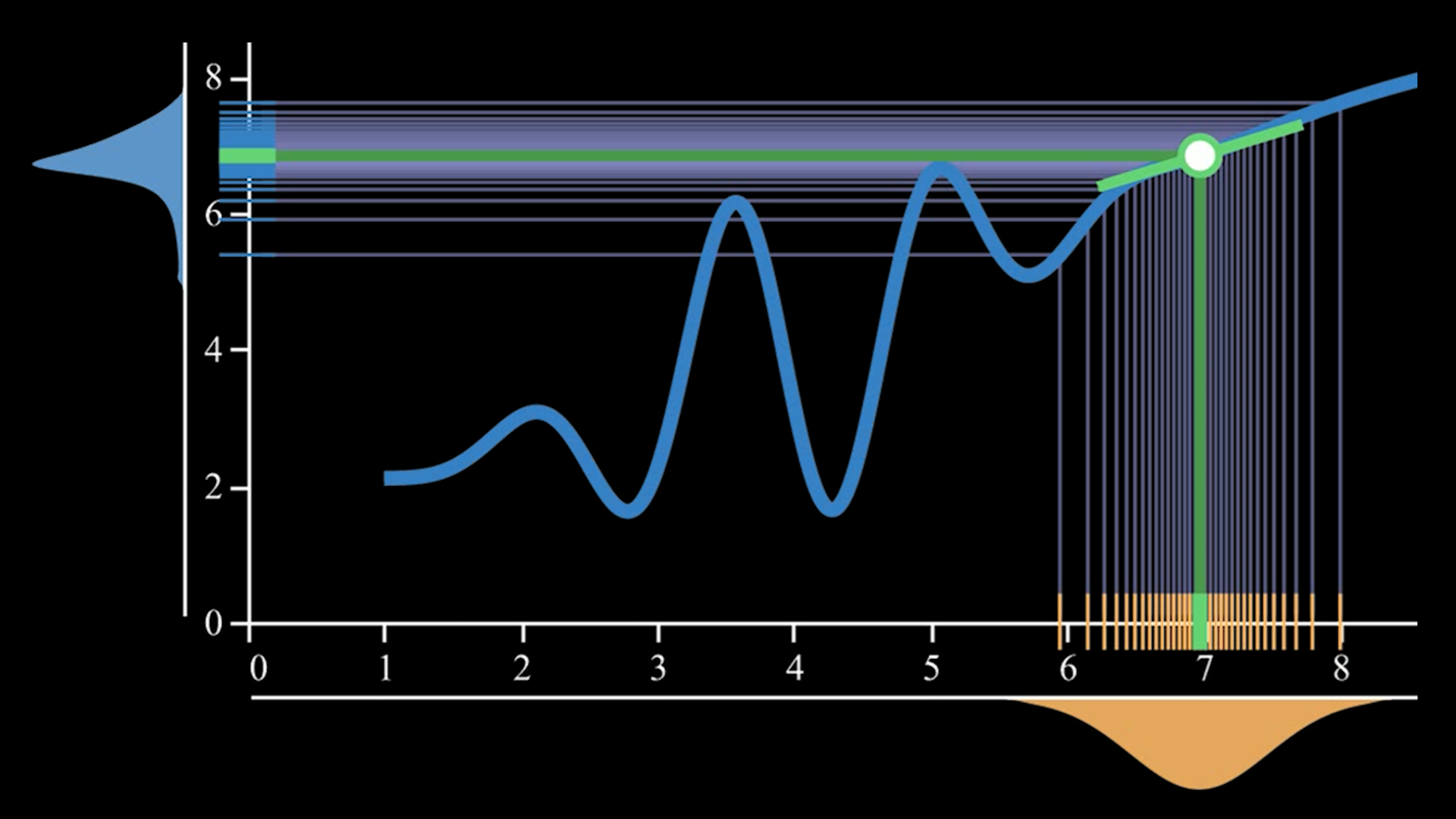
- Bayesian Optimization
- The Exponential Family
- Motivating the Gini Impurity Metric
- A Brief Explanation and Application of Gaussian Processes
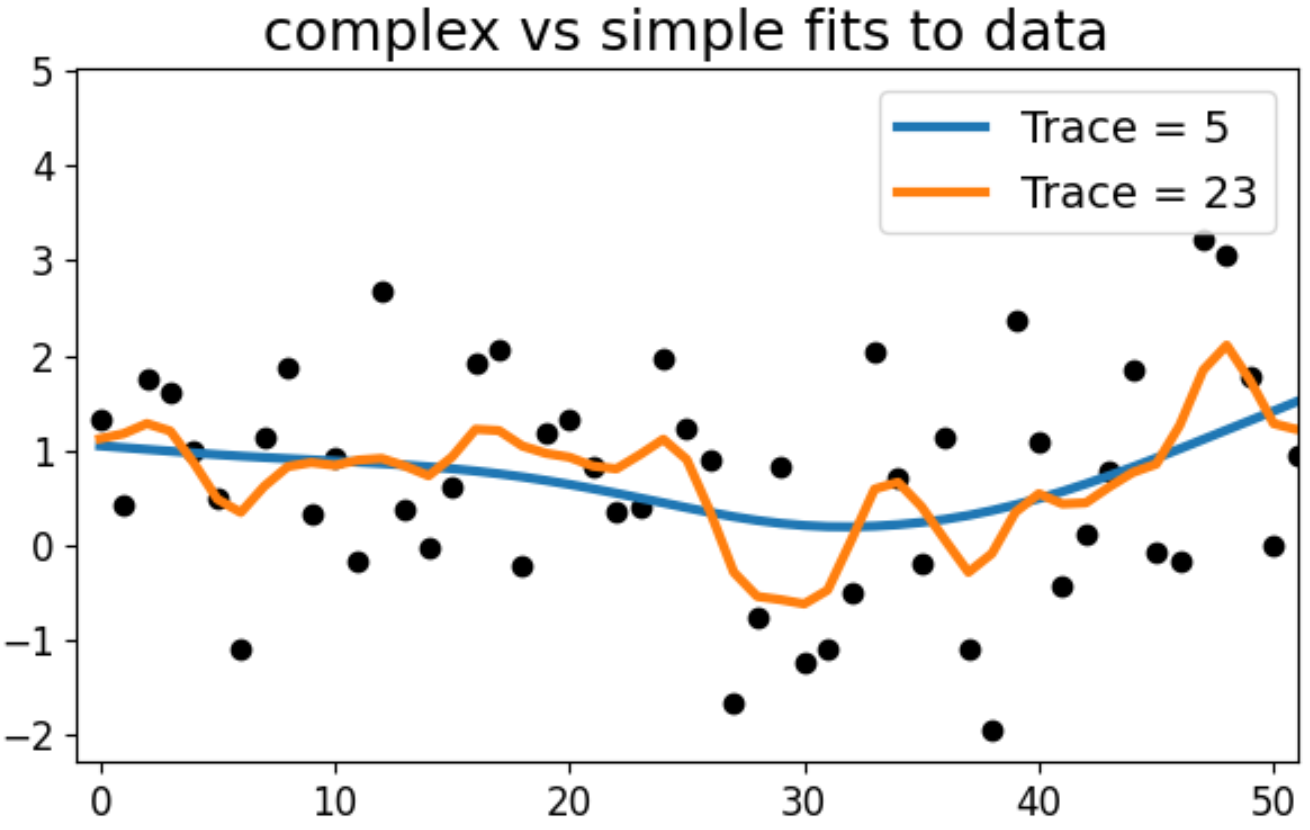
- The Trace as a Measure of Complexity